- A-
- A+
As we get older, the normally transparent crystalline lens becomes increasingly opaque. Light has difficulty passing through this lens and reaching the retina. This prevents images and colours from being correctly perceived.
Cataract does not develop evenly and at the same rate. They can form in one eye only, or more commonly in both, leading to blurred or misty vision and progressive impairment of eyesight that cannot be corrected by wearing glasses.
Other symptoms may also appear:
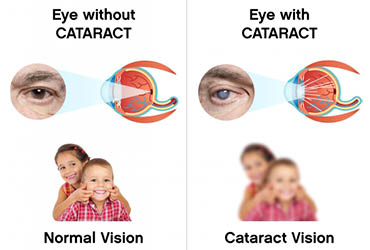 Small blotches or tiny specks in the field of vision
Small blotches or tiny specks in the field of vision
- Problems perceiving contrast, relief or colours
- Seeing things as if through a veil
- Difficulty reading and increased sensitivity to light, including glare, particularly when driving at night
- Double vision in one eye
A cataract can also have an effect on the strength of your glasses, leading to short-sightedness or making existing short-sightedness worse and therefore impairing long distance vision.
An ophthalmic exam, is crucial for reaching a diagnosis. Patients must be assisted by their ophthalmologist, who will inform them when the time has come for surgery based on the degree of visual impairment.
The only medical care which can treat cataract is the surgical operation.
Sources:
(1) Ameli, Le traitement de la cataracte [online]. Available at: www.ameli.fr/marne/assure/sante/themes/cataracte/traitement
(2) Ameli, Comprendre la cataracte [online]. Available at: www.ameli.fr/assure/sante/themes/cataracte/comprendre-cataracte.
(3) French National Health Authority, appropriate care indications and contraindications for age-related cataract surgery [online]. Available at: www.has-sante.fr/jcms/c_2906983/fr/fiche-pertinence-des-soins-indications-et-contre-indications-de-la-chirurgie-de-la-cataracte-liee-a-l-age.
(4) Bérengère Deforge, Gilles Duluc, Julie Garnon, François Mourey, Mihail Ott, « Le parcours “patient debout” - L’expérience de l’hôpital Saint-Louis », Gestions hospitalières, No. 574, March 2018.
(5) French National Health Authority, Conditions for performing cataract surgery: technical environment – Technical assessment report, July 2010 [online]. Available at: www.has-sante.fr/jcms/c_992026/fr/conditions-de-realisation-de-la-chirurgie-de-la-cataracte-environnement-technique-rapport-d-evaluation.
(6) ANAP, Premier Cercle SD - Bloc opératoire « Concilier qualité de prise en charge et efficience » - Mettre en œuvre la démarche « patient debout » au bloc opératoire [online]. Available at: http://bloc-operatoire.anap.fr/publication/2138.
(7) Jennifer Marie-Louise, Ramin Tadayoni, « Ophtalmologie : des progrès notables, des espoirs thérapeutiques, à quel coût ? », La Revue du Praticien Médecine Générale, Volume 67, no. 10, December 2017, pp. 1097-1106.
(8) Clémence Bonnet, Antoine Brezin, « Cataracte, quand opérer ? », La Revue du Praticien Médecine Générale, Volume 32, no. 1000, March 2018, pp. 326-327.



